Describe One Type of a Sigma Bond.
All the bond both sigma and pi bond in methanal are Covalent in nature. Formation of Sigma Bond.

Sigma And Pi Bonds Definition And Detailed Explanation
B the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
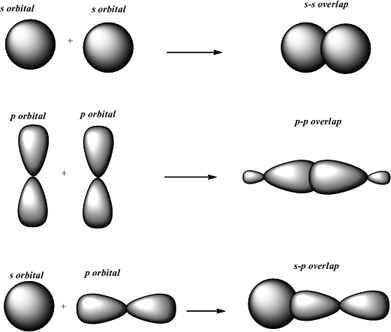
. A covalent bond formed by overlap of atomic orbitals andor hybrid orbitals along the bond axis ie along a line connected the two bonded atoms. HH bond in H2. All the bonds in ethane are σ bonds.
ZnH bond in ZnH2. The atomic orbitals overlap along the inter-nuclear axis and involve end-to-end or head-on overlap. The first covalent bond between two atoms is always a sigma bond.
The bond may be representing between two atoms either along or pie bond. This type of covalent bond is formed by the axial overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals. By this definition common forms of.
A covalent bond is best described as. In order to form sigma bond p orbitals must lie along the internuclear axis. Py dz2 axial nonlinear --- left.
It is denoted by. This type of covalent bond is formed by the lateral or sideways overlap of the atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are known to have cylindrical charge symmetry around the axis of the bond.
A the sharing of electrons between atoms. Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Thus noting that there are other possibilities the following orbital combination examples would work excluding f orbitals which are quite complex and hard to describe.
Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. The carbon forms single bond sigma bond with the two hydrogen atoms and a double bond pi bond with the oxygen atom. A the sharing of electrons.
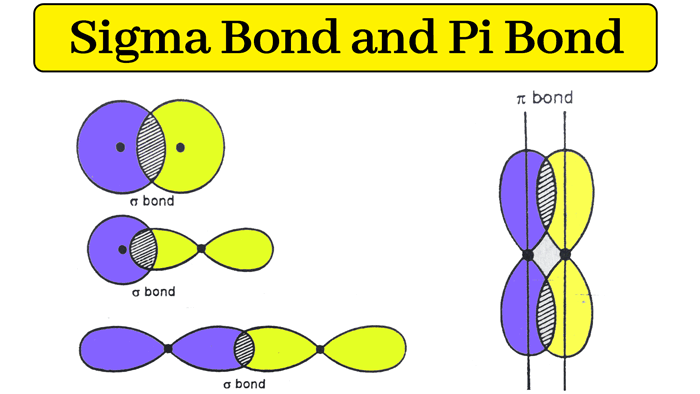
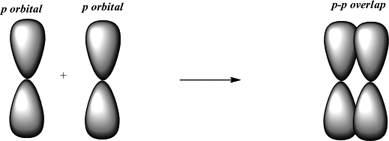
Sigma bond may be formed by any one of the following types of overlapping. Side-by-side overlap of p orbitals make. We find sigma bonds in alkanes alkenes alkynes.
The strongest covalent bond which is formed by the head-on overlapping of the atomic orbitals is called the sigma bond. Bonding interaction results by the overlapping of two atomic orbitals in the same phase whereas antibonding interaction occurs by the. There can be the free rotation of atoms around the sigma bond.
A sigma bond is formed by the end to end overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis. In a line of internuclear axis overlapping of an atomic orbital is known as a sigma bond. Sigma bonds are often formed by the combination of s orbitals in different atoms whereas pi bonds are formed from the combination of p and similar orbitals in different atoms.
C the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. This is the key difference between sigma and pi bond. In this formal approach a σ-bond is symmetrical with respect to rotation about the bond axis.
A sigma bond bond is a bond formed by the overlap of orbitals in an end-to-end fashion with the electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms. What are required for double and triple bonds. Sigma bond can be used to determine the.
Additionally the orientation of overlapping orbitals that form pi bonds will be. Only one sigma bond is formed. Py dx2y2 equatorial nonlinear.
A sigma bond is a covalent bond which is formed by the head on overlap of two atomic orbitals. Which are stronger bonds. In chemistry sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond.
S orbital overlapping with the side of a p orbital overlap of two d orbitals side by side overlap of d orbitals an attraction due to overlap of two orbitals along the internuclear axis p orbital overlapping with a d orbital. We will use hydrogen as our first example because of its simplicity. A covalent bond formed by collinear or coaxial ie.
Atoms with pi bonds are highly reactive when compared to those with only sigma bonds. Sigma and Pi bonds. Here two pi bonds can exist between two atoms.
The combination of overlapping orbitals can be s-s s-p z or p z -p z. Sigma bonding can be a bonding interaction or an antibonding interaction. Methanal formaldehyde have carbon atom as its central atom and it is bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
The molecular orbital thus formed is symmetrical about the internuclear axis and is called sigma molecular orbital. Sigma bonding is most simply defined for diatomic molecules using the language and tools of symmetry groups. D the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms.
A sigma bond and pi bond. Sigma bond-containing compound is less active. 2 Describe the formation of a pi π bond.
S orbitals are non-directional hence they can overlap in any side. Sigma σ covalent bond Axial overlap bond. I s-s over-lapping ii.
The two most common types of bonds used in our discussions. Sigma and pi are two type of bonds formed due to the overlapping two atomic orbitals. Atoms with sigma bonds are less reactive.
Sigma bond σ bond. You very likely remember these bonds from your earlier chemistry course but its usually good to take a quick review. HCl bond in HCl.
Formation of sigma bond is given below between the orbitals- ImagewillbeUploadedSoon ImagewillbeUploadedSoon As you can see above figure sigma bond is formed by the. Type of overlap Type of bond formed s and s head on s and p head on p and p head on p and p sideways. The molecular orbital is symmetrical about the internuclear axis.
Sigma bonds are a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals. No symmetry exists in pi bonds. What can only form sigma bonds.
They are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are the first bonds to form between atoms within molecules whereas pi bonds are the second. E the attraction between 2 metal atoms.
Sigma bonds and pi bonds. Axial overlapping of two atoms forms a sigma bond while lateral overlapping of two atomic orbitals forms a sigma bond. Single bond is made up of.
Thus s-s overlap always forms a sigma bond. 3 Complete the following table. A pi bond bond is a bond formed by the overlap of orbitals in a side-by-side fashion with the electron density concentrated above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms.
Describe a sigma bond. A covalent bond formed by an axial head on overlapping of half filled atomic orbital is called sigma σ bond.
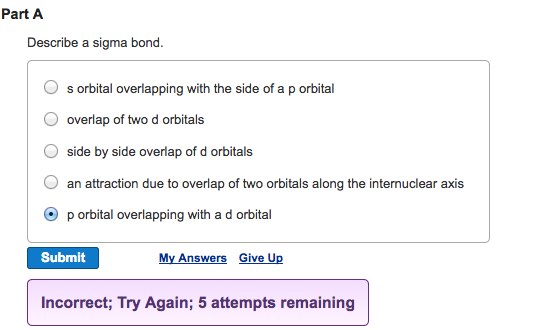
Solved Describe A Sigma Bond S Orbital Overlapping With Chegg Com

Sigma And Pi Bonds Definition And Detailed Explanation

Welcome To Chem Zipper Com What Is Sigma Bond
Hydrogen Bond Sigma Bond And Pi Bond With Example

Ib Chemistry Higher Level Notes Hybridisation

14 1 Sigma And Pi Bonds Hl Old Version Youtube
Definition Of Sigma And Pi Bonds Chegg Com
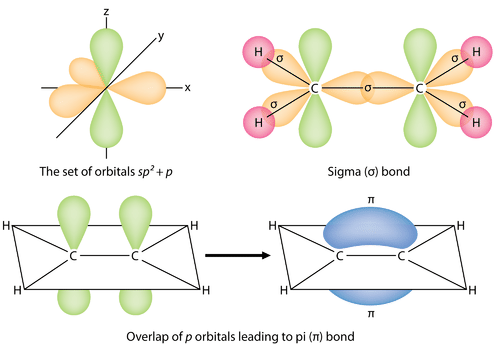
9 18 Sigma And Pi Bonds Chemistry Libretexts
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Sigma Bond S Bond
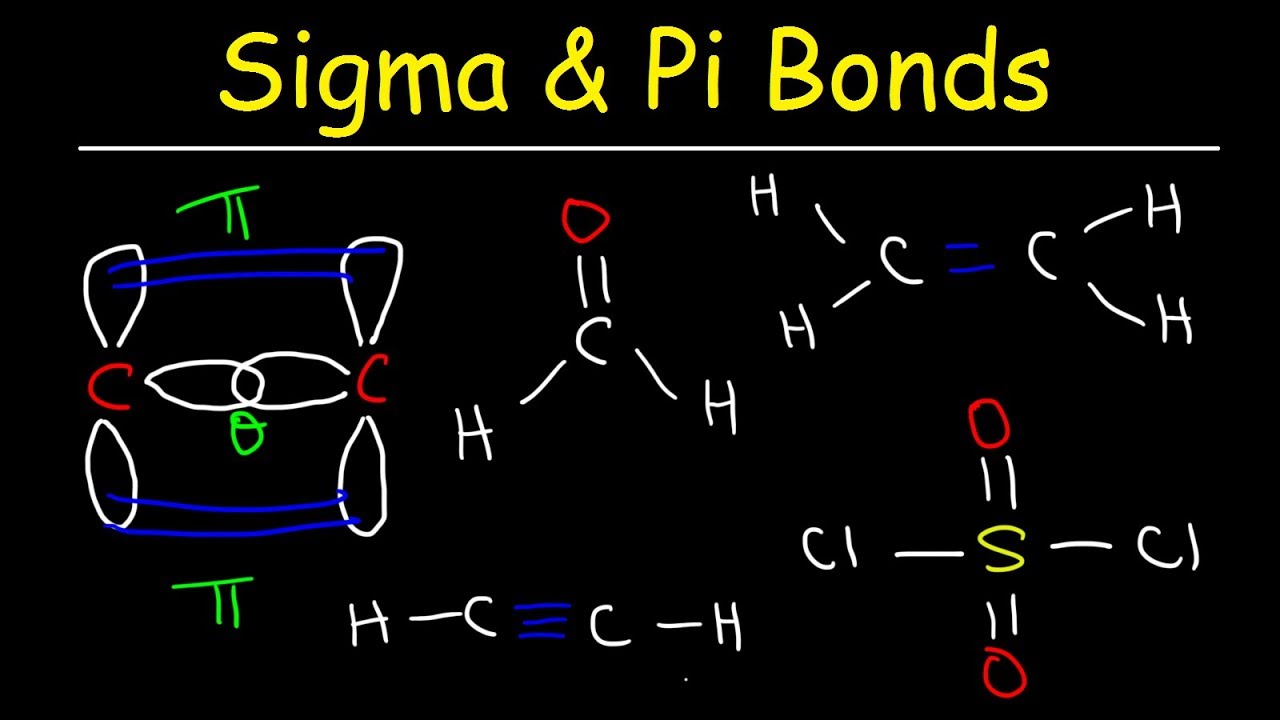
Sigma And Pi Bonds Explained Basic Introduction Chemistry Youtube

14 1 Sigma And Pi Bonds Hl New Version Youtube
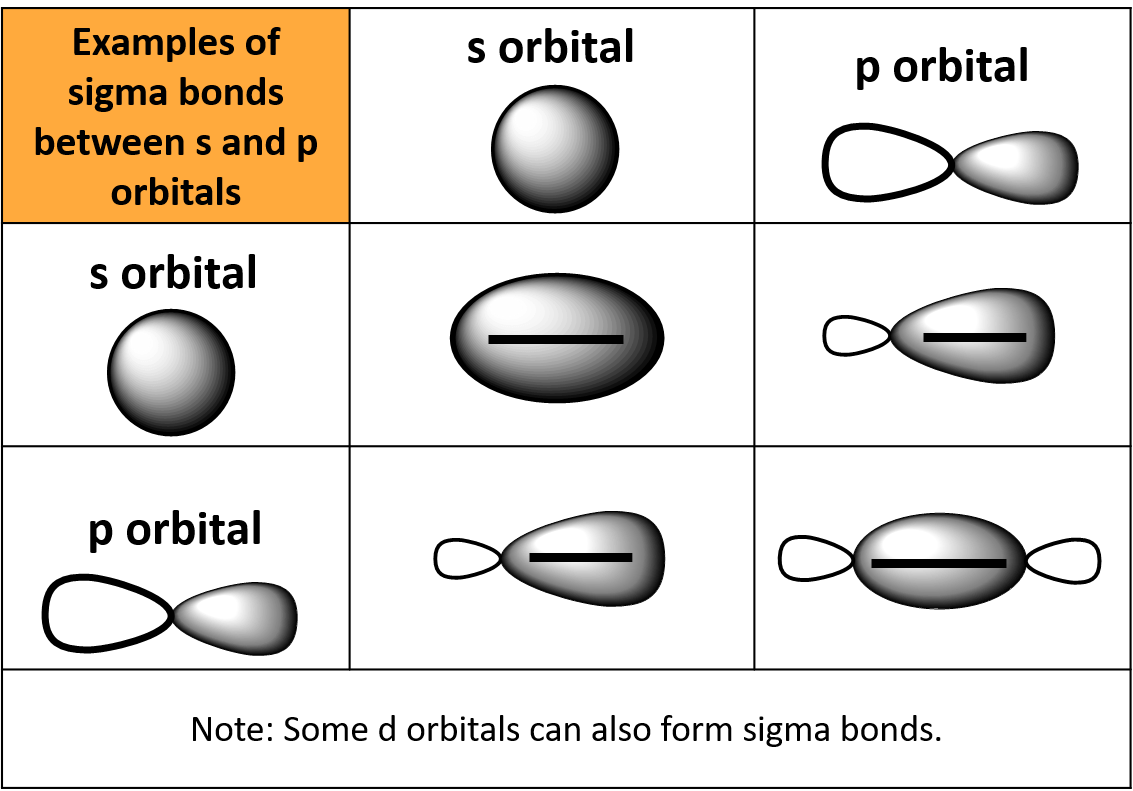
Sigma And Pi Bonds Definition Overview Expii

Definition Of Sigma And Pi Bonds Chegg Com

Sigma And Pi Bonds Brilliant Math Science Wiki

Sigma And Pi Bonds Definition Overview Expii

Solved Describe A Sigma Bond S Orbital Overlapping With The Chegg Com

Sigma And Pi Bonds Triple Bonds Chemistry Lessons Science Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

A Double Bond Consists Of A Sigma Bond And A Pi Bond Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Education
Comments
Post a Comment